75 Years of India's Independence: Post 15th August 1947, India’s journey has become a great example of an impressive growth story. The journey highlights India’s expansion ranging from agricultural production to nuclear and space technology, from affordable health care to world-class educational institutions, from Ayurveda to biotechnology, from giant steel plants to becoming an IT power, and having the third-largest start-up ecosystem in the world.
Know Your National Flag: Interesting and Amazing facts about India’s Tiranga
75 Years of India’s Independence: Historic Events, Significant Achievements & Milestones
As India is celebrating the 75th anniversary of its independence, let’s look what have been the historic events, most significant achievements and major milestones during this period:
15th August 1947: India’s Independence Day |

On 15th August 1947, India gained its independence from British Rule. Our First Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, delivered the famous 'Tryst with Destiny' speech to the Indian Constituent Assembly in the Parliament just before the clock struck 12, on August 14, 1947. On August 15, Pandit Nehru hoisted the Indian National Flag above the Lahori Gate of the Red Fort in Delhi.
26th January 1950: India became a Republic Country |

On 26th November 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India adopted the Constitution of India. Later on 26th January 1950, the Constitution of India became effective. The Constitution of India replaced the Government of India Act 1935 as the country's fundamental governing document, and the Dominion of India became the Republic of India. The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. Every year, on the 26th January, India celebrated its Republic Day.
1951: India’s First Five-year Plan was launched |

Our First Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, presented the First Five-Year Plan to the Parliament of India in 1951. The First Five-year Plan mainly focused on the development of the primary sector and was based on the Harrod–Domar model with few modifications. The motto of the first five-year plan was agricultural development. The main objective was to solve different problems that formed due to the partition of the nation. Rebuilding the country after independence was the vision of this plan.
1952: India witnessed the first Lok Sabha Election |
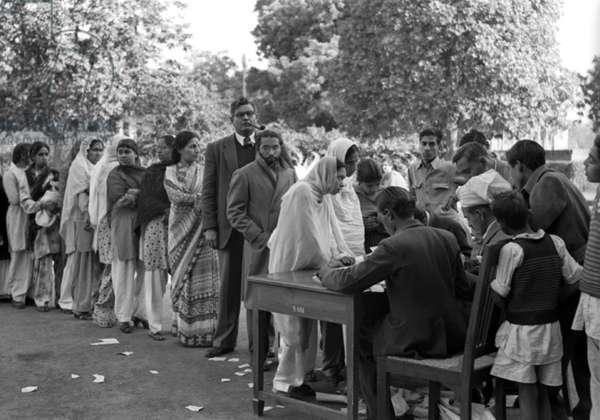

General elections were held in India between 25 October 1951 and 21 February 1952. They were the first elections to the Lok Sabha after independence in August 1947. The First Session of this Lok Sabha commenced on 13th May 1952. Total Lok Sabha seats were 489 and total eligible voters were 17.3 crores. The Indian National Congress (INC) won 364 seats. The 1st Lok Sabha lasted its full tenure of five years and was dissolved on 4th April 1957. Jawaharlal Nehru became the first democratically elected Prime Minister of India.
1953: Air India was nationalized |

Under the Air Corporations Act, 1953, Nehru nationalized nine airlines—Air India, Air Services of India, Airways (India), Bharat Airways, Deccan Airways, Himalayan Aviation, Indian National Airways, Kalinga Airlines, and Air India International—and brought them under two PSEs, Indian Airlines, and Air India International
1954: India and China signed the Panchsheel |
Panchsheel, or the Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence, were first formally enunciated in the Agreement on Trade and Intercourse between the Tibet region of China and India signed on April 29, 1954, which stated, in its preamble, that the two Governments “have resolved to enter into the present Agreement based on the following principles: -
- Mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty,
- Mutual non-aggression,
- Mutual non-interference,
- Equality and mutual benefit, and
- Peaceful co-existence.”
1955: State Bank of India (SBI) was founded |

State Bank of India was incorporated on 01 July 1955. The Government of India nationalized the Imperial Bank of India in the year 1955 with the Reserve Bank of India taking a 60% stake and the name was changed to State Bank of India.
1957: The decimalization of the rupee |

Indian coinage went decimal on April 1, 1957, ten years after it gained Independence from the British. The Indian Coinage Act was amended in September 1955 to embrace the decimal system. After the amended Act came into being, a circular issued by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India, in April 1956, said: “Government accounting with effect from April 1, 1957 is to be maintained in terms of rupees and naye paise instead of rupees, annas and pies. All challans in support of money tendered in payment of Government dues are, therefore, to be expressed in the new coinage. Similarly, all bills for withdrawals also are to be expressed in terms of rupees and naye paise.
1960: Green Revolution Began |

The Green Revolution was an endeavor initiated by Norman Borlaug in the 1960s. He is known as the 'Father of Green Revolution in the world. It led to him winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his work in developing High Yielding Varieties (HYVs) of wheat.
1961: Liberation of Goa |

The Annexation of Goa was the process in which the Republic of India annexed Estado da Índia, the then Portuguese Indian territories of Goa, Daman, and Diu, starting with the armed action carried out by the Indian Armed Forces in December 1961. In India, this action is referred to as the "Liberation of Goa".
1962: India-China War |
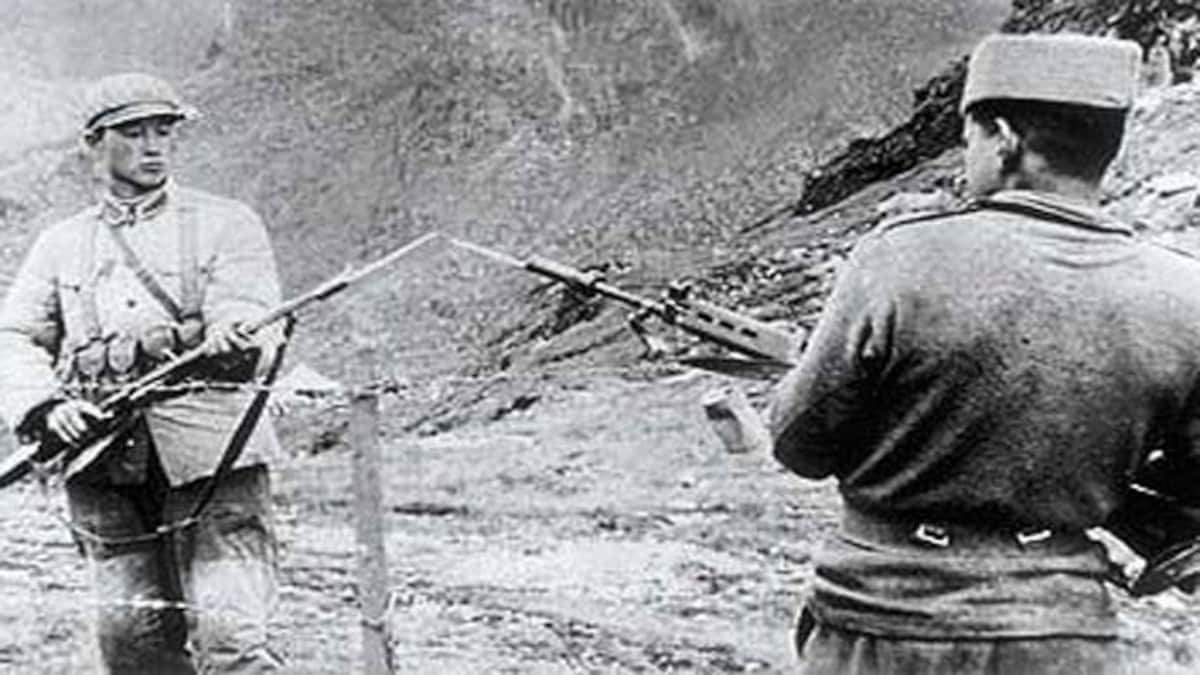

The Sino-Indian War between China and India occurred in October–November 1962. A disputed Himalayan border was the main cause of the war. The war ended when China declared a ceasefire on 20 November 1962, and simultaneously announced its withdrawal to its claimed "Line of Actual Control".
1963: India's first-ever rocket launch |

The launch of the first sounding rocket from Thumba near Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala on 21 November 1963, marked the beginning of the Indian Space Programme. Sounding rockets made it possible to probe the atmosphere in situ using rocket-borne instrumentation. This was the first milestone in modern India’s space odyssey. Dr. Vikram Sarabhai and his then accomplice Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam were the brainchild of this achievement.
1965: Indo-Pakistani War |

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 or the Second Kashmir War was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was designed to infiltrate forces into Jammu and Kashmir to precipitate an insurgency against Indian rule, It became the immediate cause of the war. On August 15, Indian forces crossed the cease-fire line. On September 20, the United Nations Security Council unanimously passed a resolution, demanding an unconditional ceasefire from both nations within 48 hours. While India immediately accepted the demand, Pakistan accepted it on September 23.
1966: Indira Gandi Became First Female PM of India |
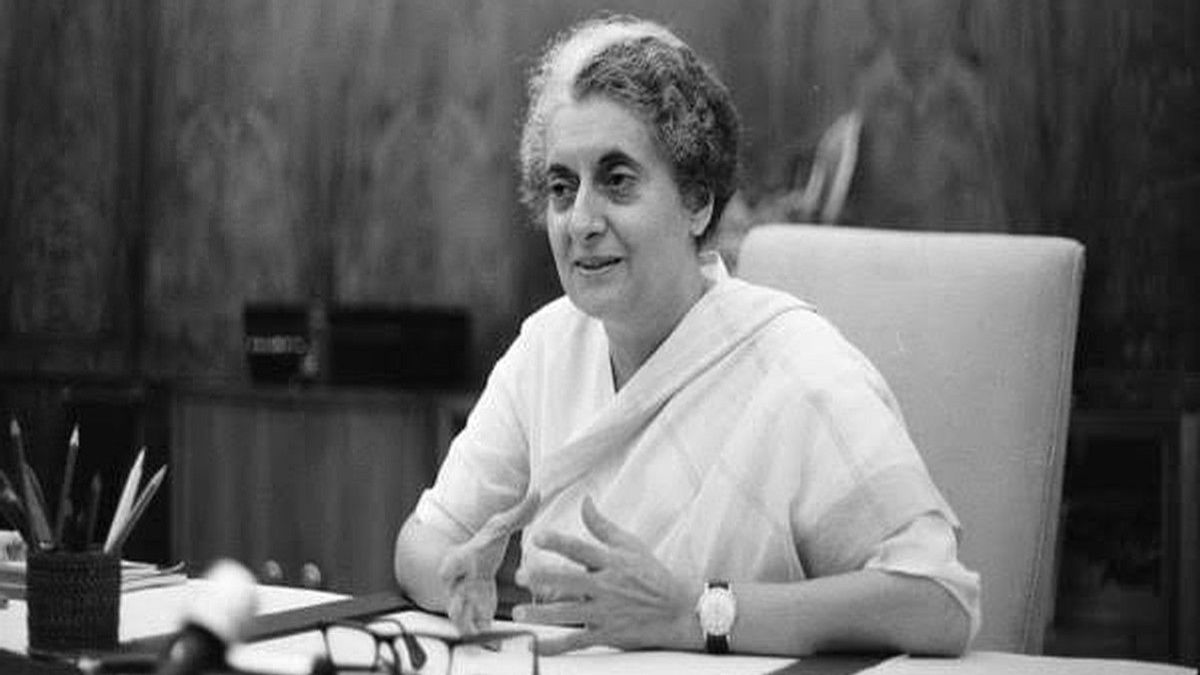

On Shastri’s sudden death in January 1966, Indira Gandhi was named leader of the Congress Party—and thus also became prime minister—in a compromise between the party’s right and left wings. Her leadership, however, came under continual challenge from the right wing of the party, led by former minister of finance Morarji Desai.
1969: Formation of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) |

ISRO was formed in 1969 with a vision to develop and harness space technology in national development while pursuing planetary exploration and space science research. ISRO replaced its predecessor, INCOSPAR (Indian National Committee for Space Research), established in 1962 by India’s first Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru and scientist Vikram Sarabhai, are considered among the founding fathers of the Indian space program.
1970: White Revolution Began |

Operation Flood, launched on 13 January 1970, was the world's largest dairy development program and a landmark project of India's National Dairy Development Board.
1971: India-Pakistan War |

The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 was a military confrontation between India and Pakistan that occurred during the Bangladesh Liberation War in East Pakistan from 3 December 1971 to the fall of Dacca (Dhaka) on 16 December 1971.
1975: The Emergency was imposed |

The Emergency in India was a 21-month period from 1975 to 1977 when Prime Minister Indira Gandhi declared a state of emergency across the country. Officially issued by President Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed under Article 352 of the Constitution because of the prevailing "internal disturbance", the Emergency was in effect from 25 June 1975 until its withdrawal on 21 March 1977. Elections were canceled, civil liberties were suspended, most of Indira Gandhi's political opponents were imprisoned and the press was censored. Numerous human rights were violated during that period. The Emergency is one of the most controversial periods of independent India's history.
1982: Colour television began its journey in India |

DD became national when it started to telecast national programs in the year 1982. In the same year, color TVs were introduced in the Indian markets. The first color programs were the live telecast of the Independence Day parade on 15th August 1982, followed by the Asian Games being held in Delhi.
1983: India won the cricket World Cup for the first time |

On 25th June 1983, the Indian Cricket Team created history for the first time by winning the World Cup by defeating West Indies who had won the last two world cup. India’s Victory in 1983 is considered to be the landmark moment in Cricket History. 83 World cup was played in Lord's Stadium (England). For the first time, an Asian Nation-India reached the World Cup Final and this was the third consecutive World Cup final appearance for the West Indies.
Check 1983 Cricket World Cup Indian Squad
1987: Goa became one of the States of India |

On 30 May 1987, Goa attained statehood (while Daman and Diu became a separate union territory), and Goa was reorganized into two districts, North Goa and South Goa. Dayanand Bandodkar was elected as the first Chief Minister of Goa, Daman, and Diu. Goa became India's 25th state on 30th May 1987.
1988: The SEBI was established |
The Securities and Exchange Board of India was constituted on April 12, 1988, as a non-statutory body through an Administrative Resolution of the Government for dealing with all matters relating to the development and regulation of the securities market and investor protection and to advise the Government on all these matters.
1989: Agni Missile was successfully launched |

Agni-I was first tested at the Interim Test Range in Chandipur at 7:17 AM on 22 May 1989 and was capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) or a nuclear warhead. Agni missiles consist of one (short range) or two stages (intermediate-range).
1991: Economic Liberalisation in India |

The three branches of the new economic policy of 1991 were Liberalization, Privatization, and Globalization. The immediate factor that triggered India's economic reforms of 1991 was a severe balance of payments crisis that occurred in the same year. The first signs of India's balance of payments crisis became evident in late 1990 when foreign exchange reserves began to fall.
1995: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited was founded |

The Government of India under Prime Minister H.D. Deve Gowda[19] and the Government of Delhi jointly set up a company called the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) on 3 May 1995, with Elattuvalapil Sreedharan as the managing director.
1998: India conducted Pokhran-II tests |

On 11 and 13 May 1998, twenty-four years after Pokhran-I, the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) conducted five further nuclear tests, dubbed "Pokhran-II", at the Pokhran range. The chief scientific adviser and the Director of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Dr. Abdul Kalam, and Dr. R. Chidambaram, the Director of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), were the chief coordinators of this test planning.
1999: Kargil War |

The Kargil War, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control. On 26th July 1999, India marked the successful completion of “Operation Vijay” by declaring victory over Pakistan in the Kargil war, ending the three-month war along the Line of Control. The day since then has been celebrated as “Kargil Vijay Diwas”.
2000: Jharkhand became India's 26th state |
Jharkhand was carved out of 18 districts of Bihar in the year 2000 on November 15. Later, six more districts were carved out by reorganizing the existing districts.
2007: First Woman President of India |

Pratibha Patil is an Indian politician and lawyer, who was the first woman to serve as president of India from 2007-2012.
2008: Chandrayaan-1 launched |

Chandrayaan-1 was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program which was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on October 22, 2008. The mission was a major boost to India's space program, as our country researched and developed its own technology to explore the Moon.
2010: Education became a fundamental right of children |
The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act or Right to Education Act (RTE) is an Act of the Indian Parliament that was enacted on August 4, 2009. It describes the modalities of the importance of free and compulsory education for children between the age of 6 to 14 years in India under Article 21A of the Indian Constitution. When the Act came into force on April 1, 2010, India became one of the countries in the world to make education a fundamental right.
2015: NITI Aayog was formed |

The NITI Aayog, the apex public policy think tank of the Indian government, and the nodal agency tasked with catalyzing economic development, and fostering cooperative federalism through the involvement of state governments of the country in the economic policy-making process, was established on January 1, 2015.
2017: GST was launched by the Indian government |
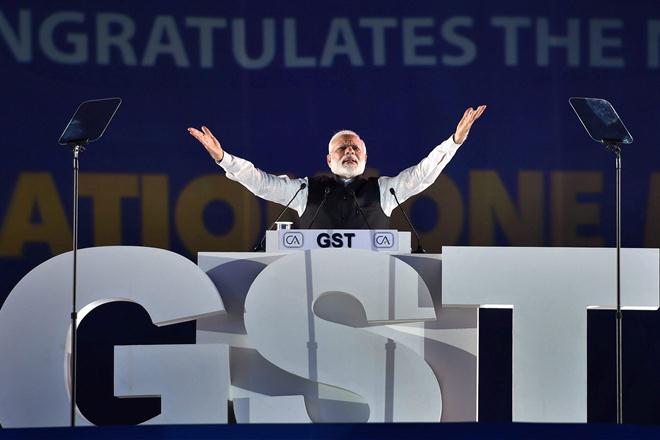

The Goods and Services Tax, popularly known as GST, was launched at midnight on July 1, 2017, by the President of India, and the Government of India. It was marked by a historic midnight (June 30- July 1) session of both the Houses of Parliament convened at the Central Hall, and it was attended by high-profile guests from the business and the entertainment industry.
2020: COVID-19 Pandemic and India’s lockdown |
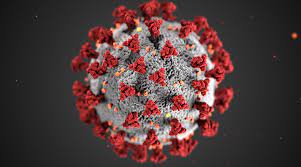
In 2020, India witnessed the COVID-19 pandemic and people were confined to their homes because of the resultant lockdown. The tale of lockdown began on the evening of March 24, 2020, when the Government of India ordered a nationwide lockdown for 21 days, limiting the movement of the entire population to thwart the outbreak of the pandemic. It came after a 14-hour voluntary public curfew on March 22, followed by enforcement of a series of regulations in the COVID-19-affected regions in the country.
2022: India gets its first tribal President |

Draupadi Murmu took oath as the 15th President of India on July 25, 2022. She contested against Yashwant Sinha, the joint opposition’s nominee for the top constitutional job. Draupadi Murmu is a tribal leader from Rairangpur in the Mayurbhanj district in Odisha
Check Draupadi Murmu Biography
On the 75th Independence Day of India, people are celebrating Azadi ka Mahotsav to acknowledge the development and growth of India post Independence. Democracy has ensured that virtually every region of India and every group is represented at the highest levels of office in India. Women leaders have been elected as Prime Minister, President and Speaker of the Indian parliament, and chief ministers of several of India’s large states.

